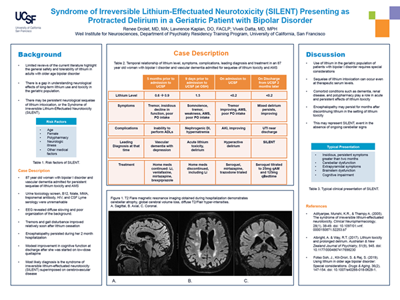
Syndrome Of Irreversible Lithium-effectuated Neurotoxicity
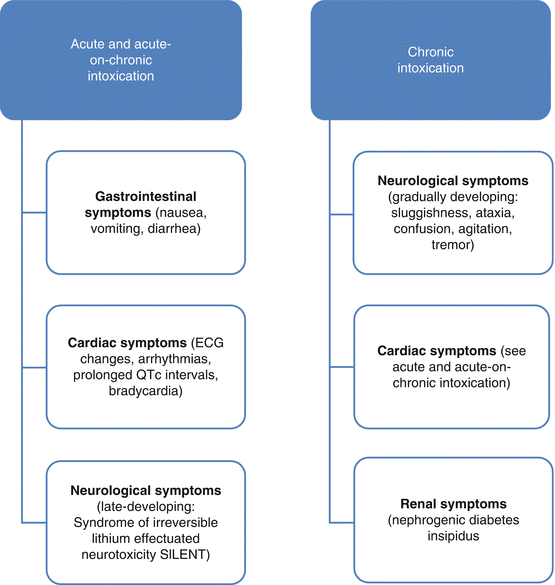
Syndrome of irreversible lithium-effectuated neurotoxicity. Symptoms may include a tremor increased reflexes trouble walking kidney problems and an altered level of consciousness. The most important being neurotoxicity which may occur at therapeutic levels when other drugs which act centrally on the CNS are taken concurrently. Lithium toxicity can occur due to excessive intake or decreased.
SILENT is more common with chronic intoxication than acute toxicity. Lithium toxicity also known as lithium overdose is the condition of having too much lithium. Syndrome of irreversible lithium effectuated neurotoxicity SILENT encephalopathy stupor seizures.
Manifestations may include cerebellar dysfunction and cognitive dysfunction. Persistent sequelae of lithium intoxication gained clinical attention in the 1980s and were named Syndrome of Irreversible Lithium-Effectuated Neurotoxicity SILENT. Some symptoms may last for a year after levels return to normal.
Complications may include serotonin syndrome. The authors review the published cases of SILENT reported in the literature and discuss various clinical manifestations. SILENT Syndrome of Irreversible Lithium-Effectuated NeuroToxicity Potentially permanent neurologic injury resulting from lithium toxicity due to an unclear mechanism.
The authors inclusion criteria included persistence of sequelae for at least 2 months. Brugada syndrome or family history of Brugada syndrome see section 44.
Persistent sequelae of lithium intoxication gained clinical attention in the 1980s and were named Syndrome of Irreversible Lithium-Effectuated Neurotoxicity SILENT.
Lithium toxicity can occur due to excessive intake or decreased. The authors inclusion criteria included persistence of sequelae for at least 2 months. The authors review the published cases of SILENT reported in the literature and discuss various clinical manifestations. Lithium toxicity also known as lithium overdose is the condition of having too much lithium. Manifestations may include cerebellar dysfunction and cognitive dysfunction. Complications may include serotonin syndrome. Syndrome of irreversible lithium effectuated neurotoxicity SILENT encephalopathy stupor seizures. Lithium toxicity can occur due to excessive intake or decreased. Brugada syndrome or family history of Brugada syndrome see section 44.
The authors review the published cases of SILENT reported in the literature and discuss various clinical manifestations. Lithium toxicity can occur due to excessive intake or decreased. The authors inclusion criteria included persistence of sequelae for at least 2 months. Brugada syndrome or family history of Brugada syndrome see section 44. Lithium toxicity also known as lithium overdose is the condition of having too much lithium. The authors review the published cases of SILENT reported in the literature and discuss various clinical manifestations. Complications may include serotonin syndrome.

































Posting Komentar untuk "Syndrome Of Irreversible Lithium-effectuated Neurotoxicity"