Artificially Stimulating Antibodies To A Disease Is Called _____.
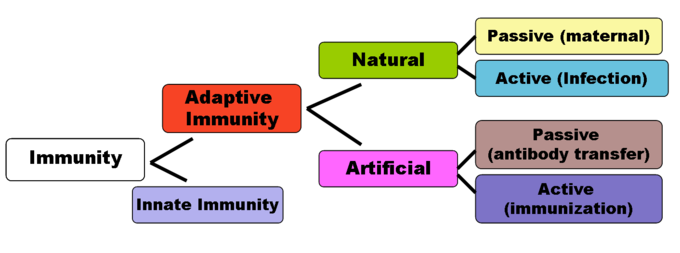
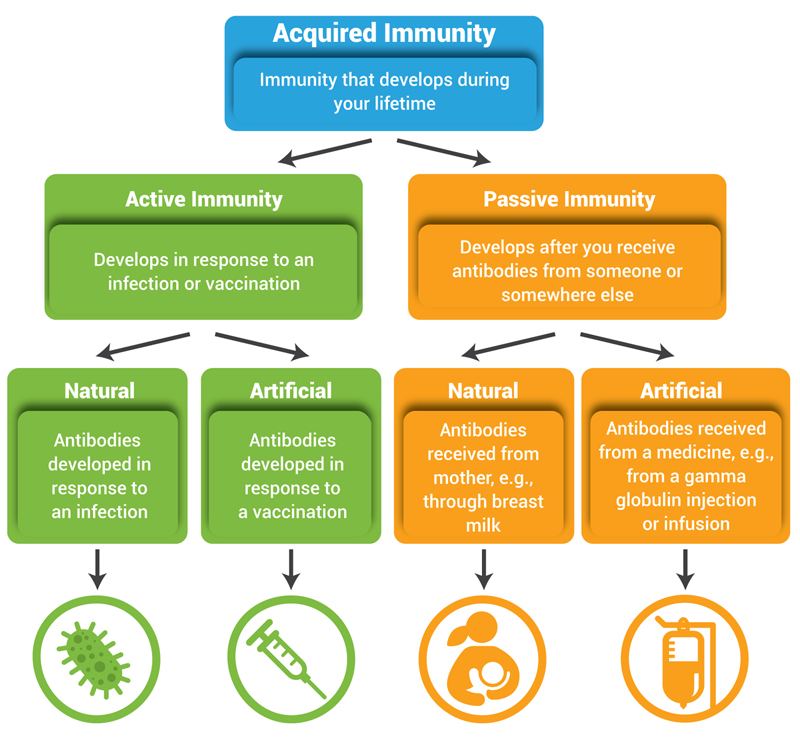
Artificially stimulating antibodies to a disease is called _____.. This is due to a rare phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement ADE. Artificially stimulating antibodies to a disease is called immunization. Active Artificially Acquired Immunity Active artificially acquired immunity refers to any immunization with an antigen.
Immunization is the process by which an individuals immune system becomes fortified. They are found in plasma the liquid part of blood and lymph other body fluids and in the membrane of certain cells. Antibodies that bind to.
Most people with Hashimoto disease have high levels of both Tg and TPO antibodies. Such a hybrid cell is called a hybridoma. First artificially supplying antibodies might make an infection worse.
The antibodies it tests for are present in 90 of the people who have this disease. As a consequence of their in vitro manufacturing method the antigen recognition site of synthetic antibodies can be engineered to any desired target and may extend beyond the typical immune repertoire offered by natural antibodies. Synthetic antibodies are affinity reagents generated entirely in vitro thus completely eliminating animals from the production process.
Synthetic antibodies include recombinant antibodies nucleic acid aptamers and non-immunoglobulin protein scaffolds. Specifically immunoglobulins are the special proteins that function as antibodies. Depending on their action antibodies are called agglutinins precipitins bacteriolysins antitoxins and opsonins.
These antibodies mimic the action of TSH resulting in TSHR stimulation and hyperthyroidism and have been associated with GD-associated extrathyroidal manifestations. The foreign substance usually a protein is called an antigen that is one that generates the production of an antagonist. Artificial production of monoclonal antibodiesThe technique involves fusing certain myeloma cells cancerous B cells which can multiply indefinitely but cannot produce antibodies with plasma cells noncancerous B cells which are short-lived but produce a desired antibody.
The most common response to the antigen is the production of antibody. This transfer of antibodies may be done as a prophylactic measure ie to prevent disease after exposure to a pathogen or as a strategy for treating an active infection.
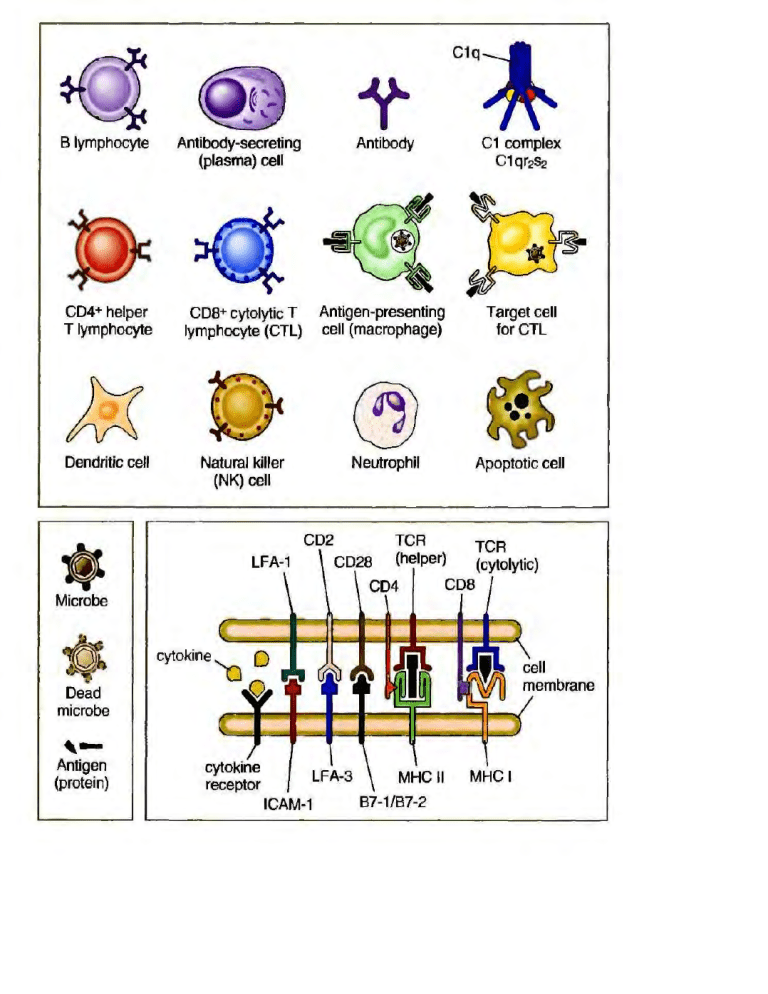
An antibody Ab also known as an immunoglobulin Ig is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as pathogenic bacteria and virusesThe antibody recognizes a unique molecule of the pathogen called an antigen.
These antibodies can be a sign of Graves disease. The most common response to the antigen is the production of antibody. Artificial passive immunity refers to the transfer of antibodies produced by a donor human or animal to another individual. Artificial production of monoclonal antibodiesThe technique involves fusing certain myeloma cells cancerous B cells which can multiply indefinitely but cannot produce antibodies with plasma cells noncancerous B cells which are short-lived but produce a desired antibody. They are found in plasma the liquid part of blood and lymph other body fluids and in the membrane of certain cells. During a vaccination the antigen of a pathogen is introduced into the body and stimulates the immune system to develop a. These antibodies can be a sign of Graves disease. This is due to a rare phenomenon called antibody-dependent enhancement ADE. These antibodies can also be a sign of Hashimoto disease.
Synthetic antibodies are affinity reagents generated entirely in vitro thus completely eliminating animals from the production process. TSH binding inhibition assays and bioassays for measurement of TSHR antibody. Depending on their action antibodies are called agglutinins precipitins bacteriolysins antitoxins and opsonins. They are found in plasma the liquid part of blood and lymph other body fluids and in the membrane of certain cells. These antibodies mimic the action of TSH resulting in TSHR stimulation and hyperthyroidism and have been associated with GD-associated extrathyroidal manifestations. Artificially stimulating antibodies to a disease is called immunization. Thyroid-stimulating hormone TSH receptor.
































Posting Komentar untuk "Artificially Stimulating Antibodies To A Disease Is Called _____."