How Can Biofilm Formation Impact Treatment Of Infectious Disease
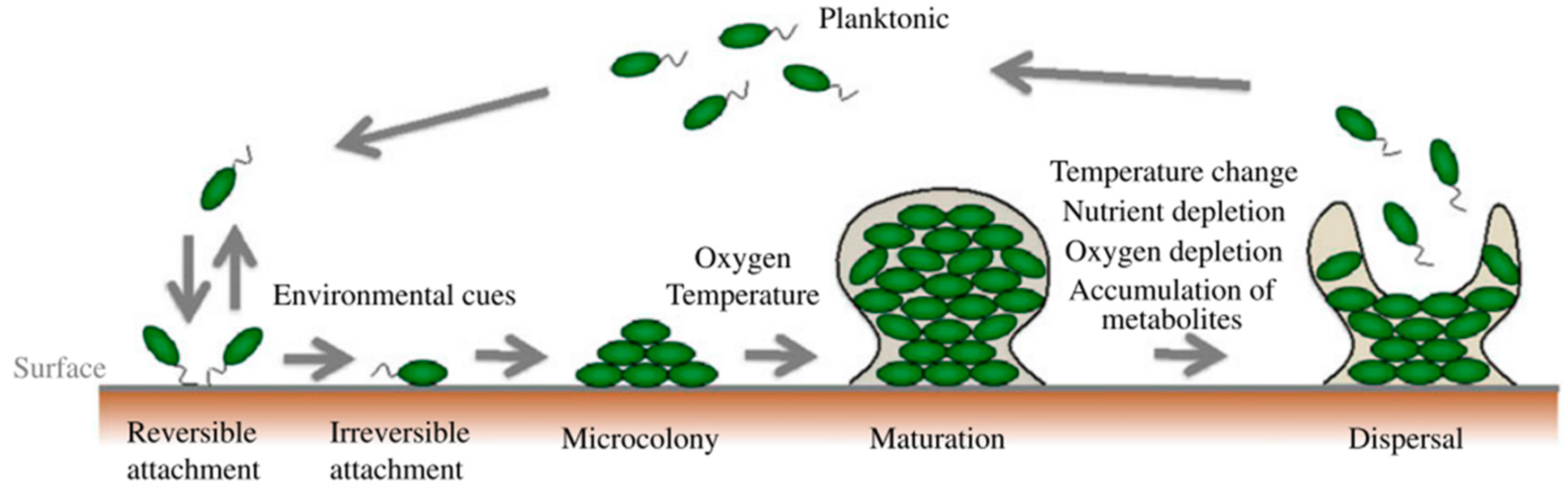
How can biofilm formation impact treatment of infectious disease. However in cases where the bacteria succeed in forming a biofilm within the human host the infection often turns out to be untreatable and will develop into a chronic state. Under the protection of biofilm microbial cells in biofilm become tolerant and resistant to antibiotics and the immune responses which increases the difficulties for the clinical treatment of biofilm. Formation of biofilm is a survival strategy for bacteria and fungi to adapt to their living environment especially in the hostile environment.
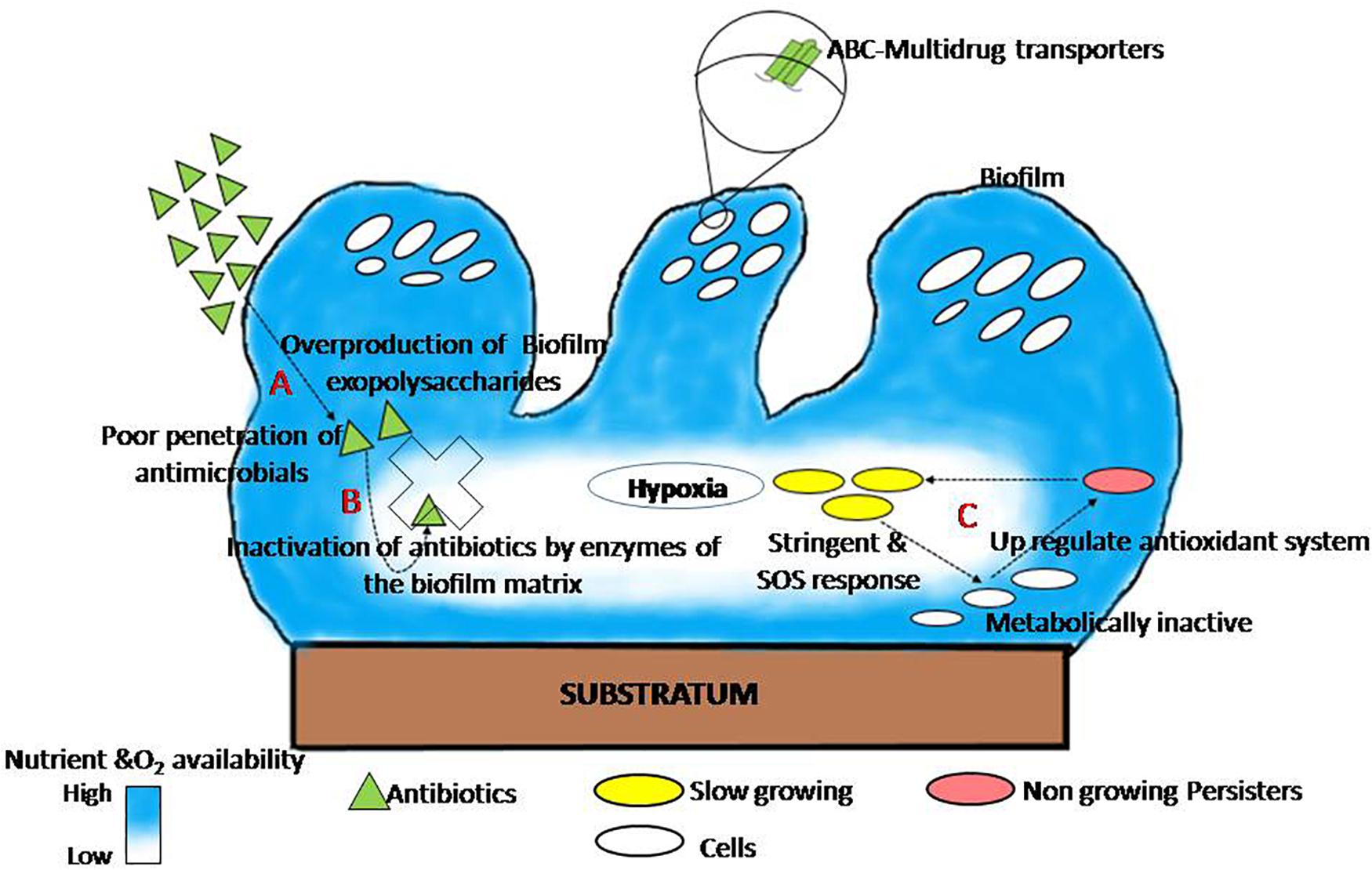
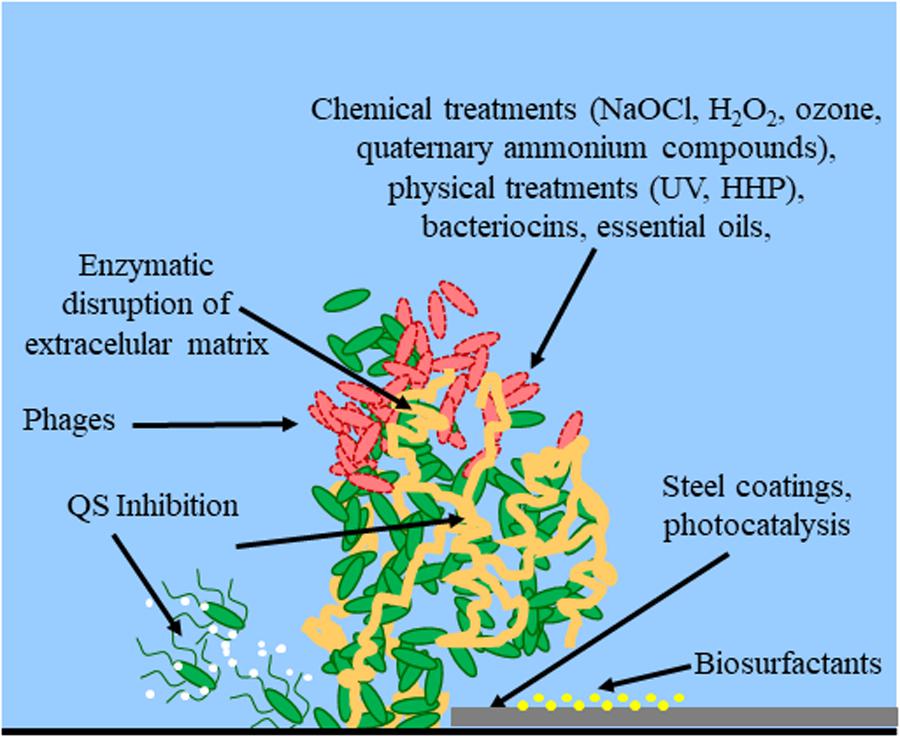
Nitric oxide has also been shown to trigger the dispersal of biofilms of several bacteria species at sub-toxic concentrations. Nitric oxide has potential as a treatment for patients that suffer from chronic infections caused by biofilms. Bacterial biofilms are resistant to antibiotics disinfectant chemicals and to phagocytosis and other components of the innate and adaptive inflammatory defense system of the body.
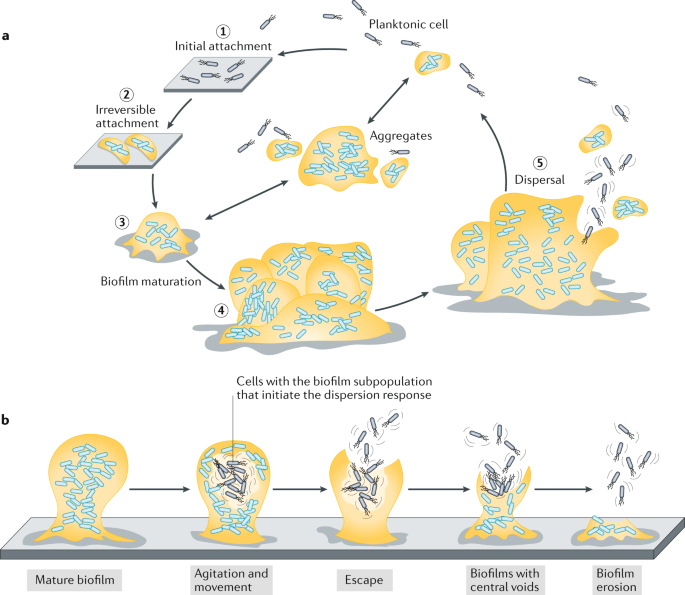
It was generally assumed that cells dispersed from biofilms immediately go into the planktonic growth phase. Transitioning from acute to chronic infection is frequently associated with biofilm formationBacteria in biofilms are innately more resistant to antimicrobial agents. The National Institutes of Health NIH revealed that among all microbial and chronic infections 65 and 80 respectively are associated with biofilm formation.
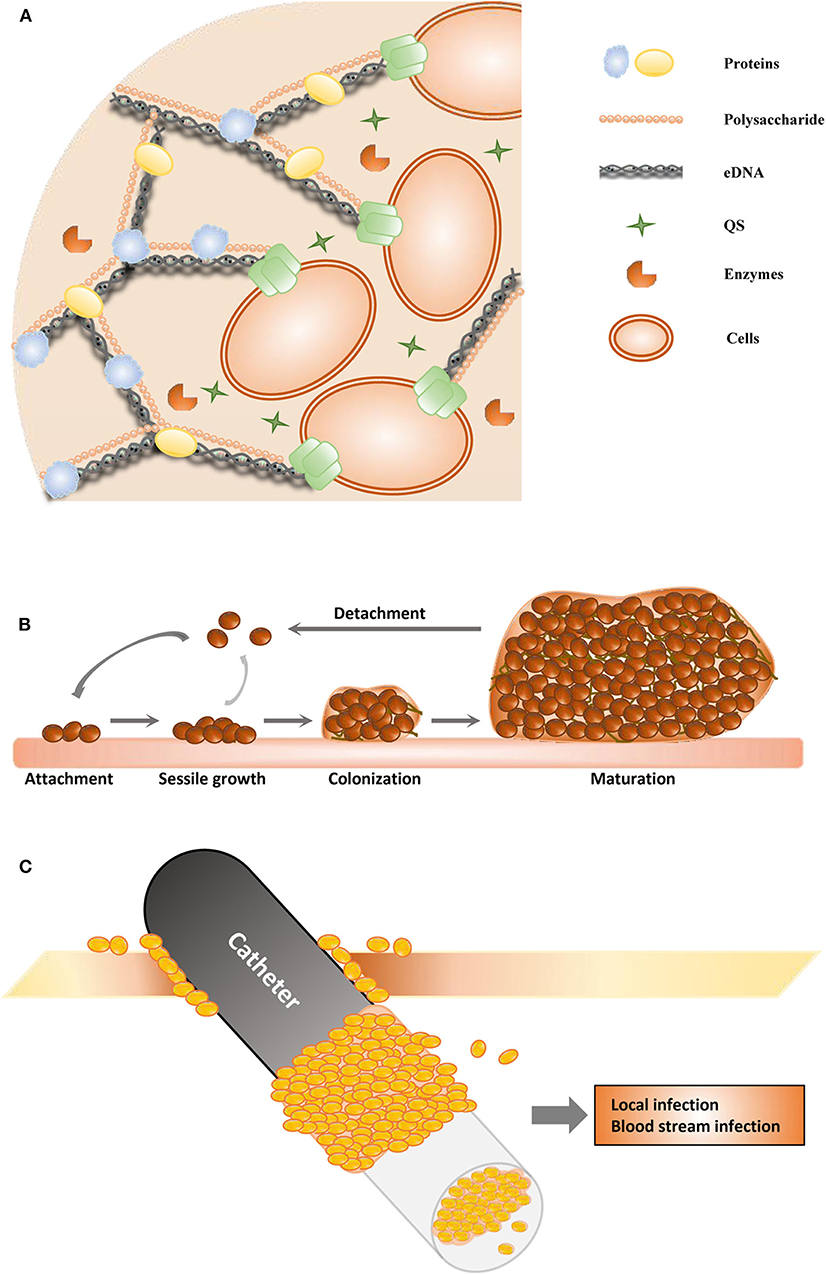
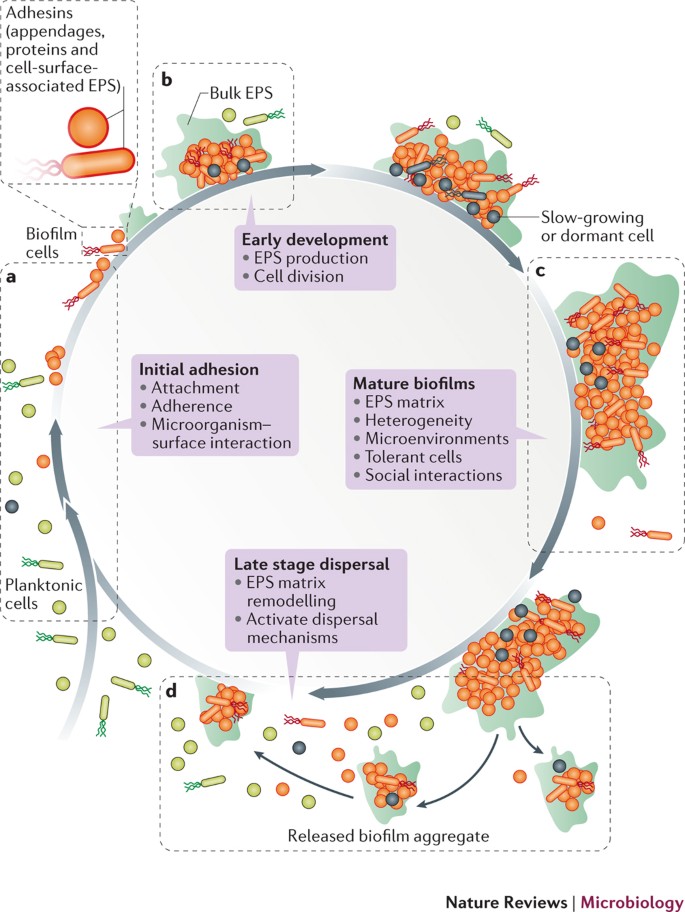
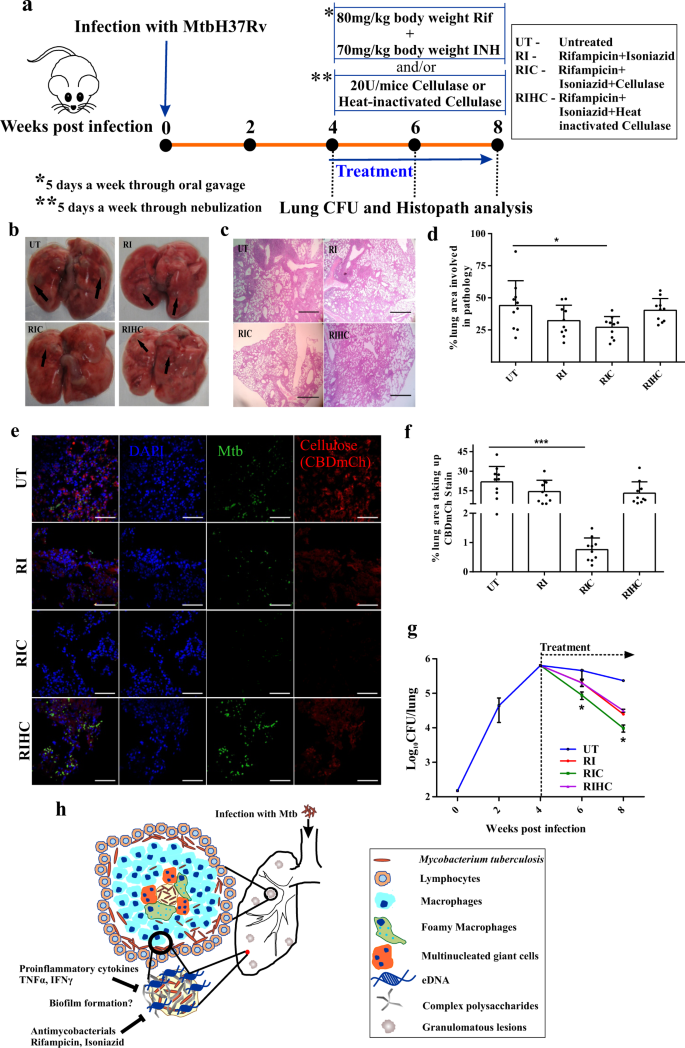
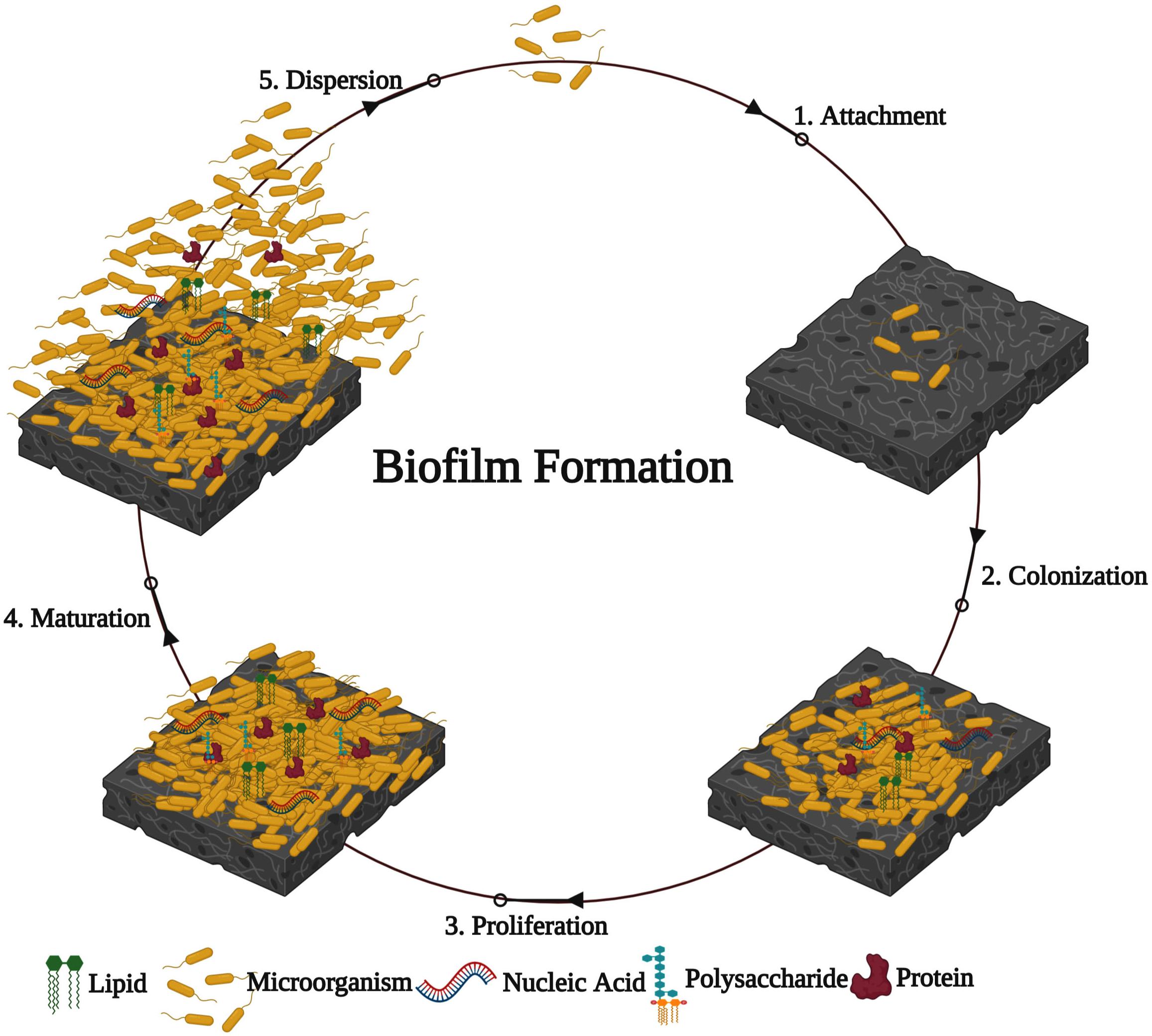
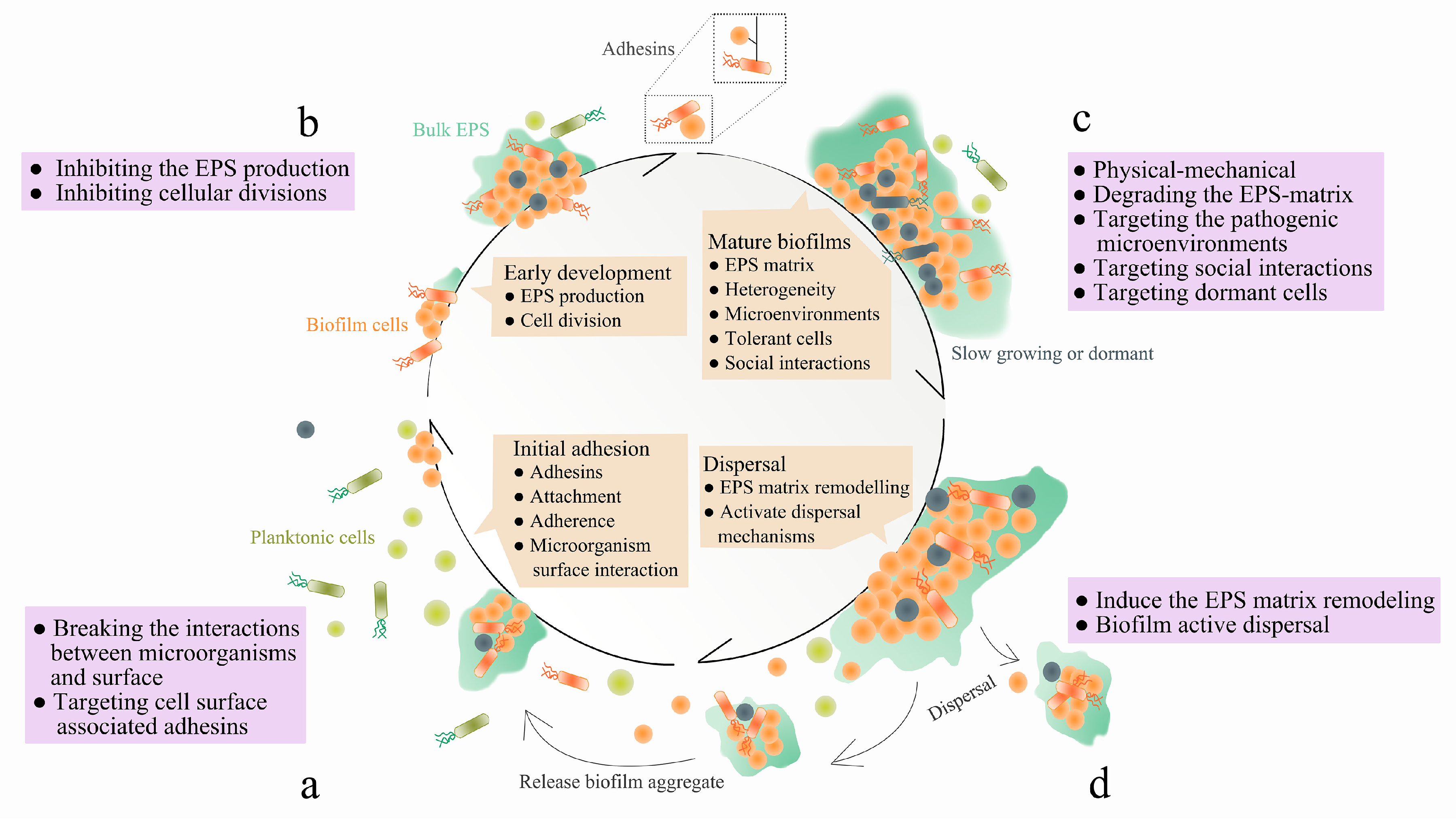
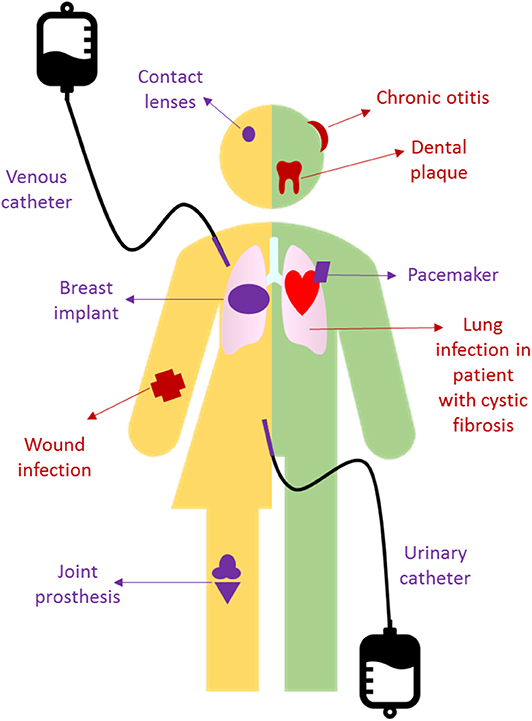
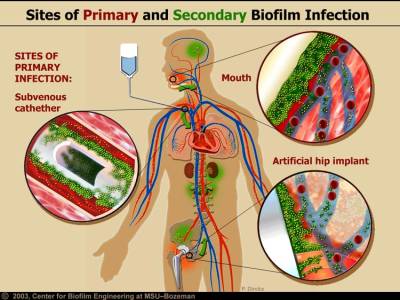
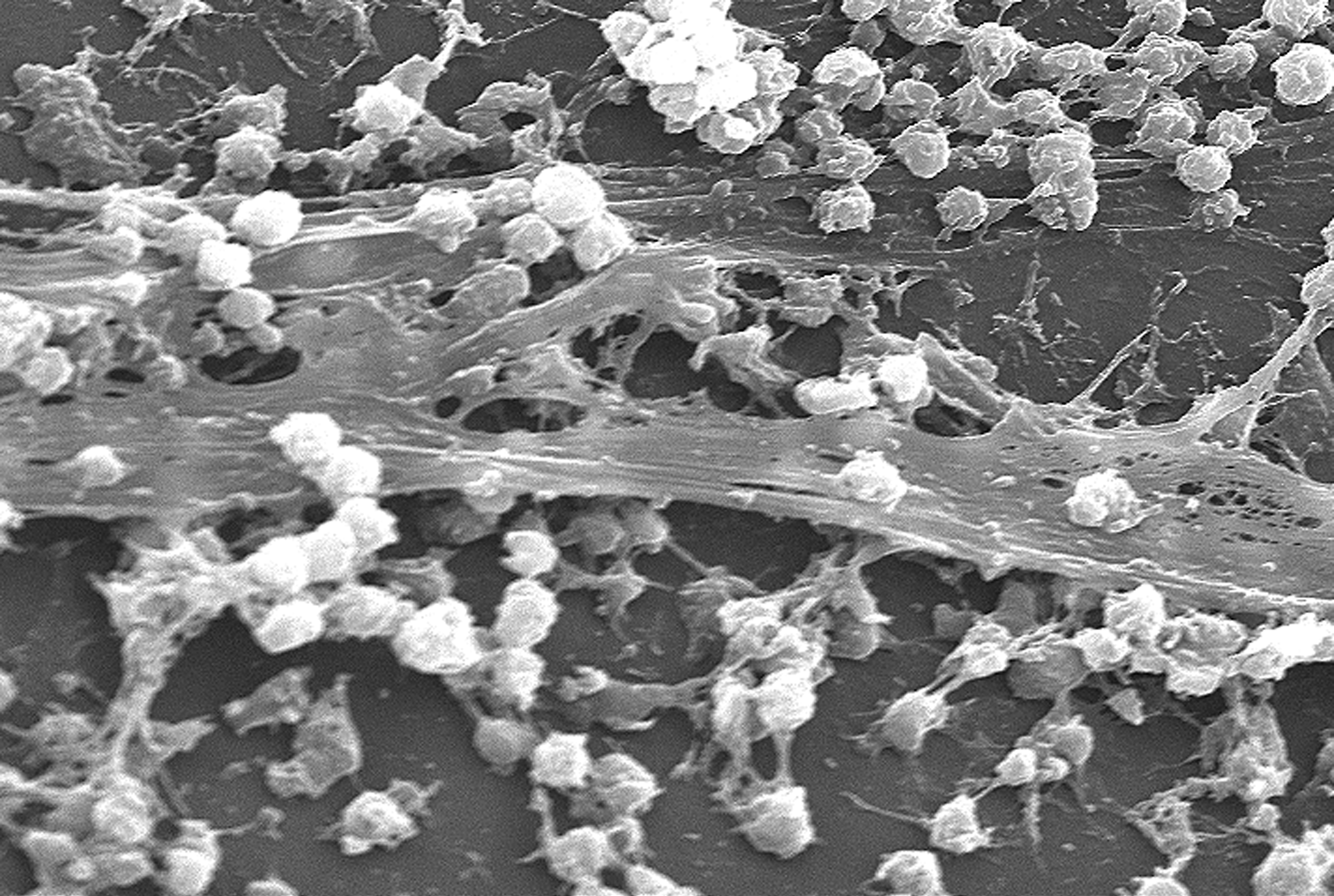
Characteristics of biofilms that can be important in infectious disease processes include a detachment of cells or biofilm aggregates may result in bloodstream or urinary tract infections or in the production of emboli b cells may exchange resistance plasmids within biofilms c cells in biofilms have dramatically reduced susceptibility to antimicrobial agents d biofilm-associated. It is important to note that A biofilm is a structured consortium of bacteria embedded in a self-produced polymer matrix consisting of polysaccharide protein and extracellular DNA. The impact of a foreign implant on the infection process was already recognized in 1956 as the presence of a foreign material required a 7510 4 lower dose of Staphylococcus aureus to cause a subcutaneous infection in humans which even then did not resolve 3.
DISCUSSION 02 What do you think are the most important changes in chemotherapeutic management of microbial disease. The presence of indwelling medical devices increases the risk for biofilm formation and subsequent infection. Kindly login to access the content at no cost.
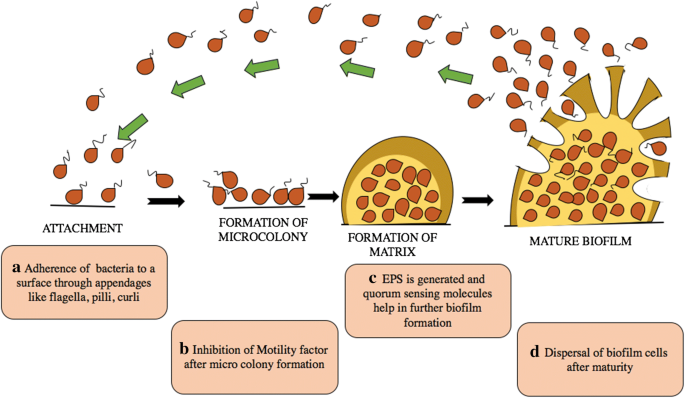
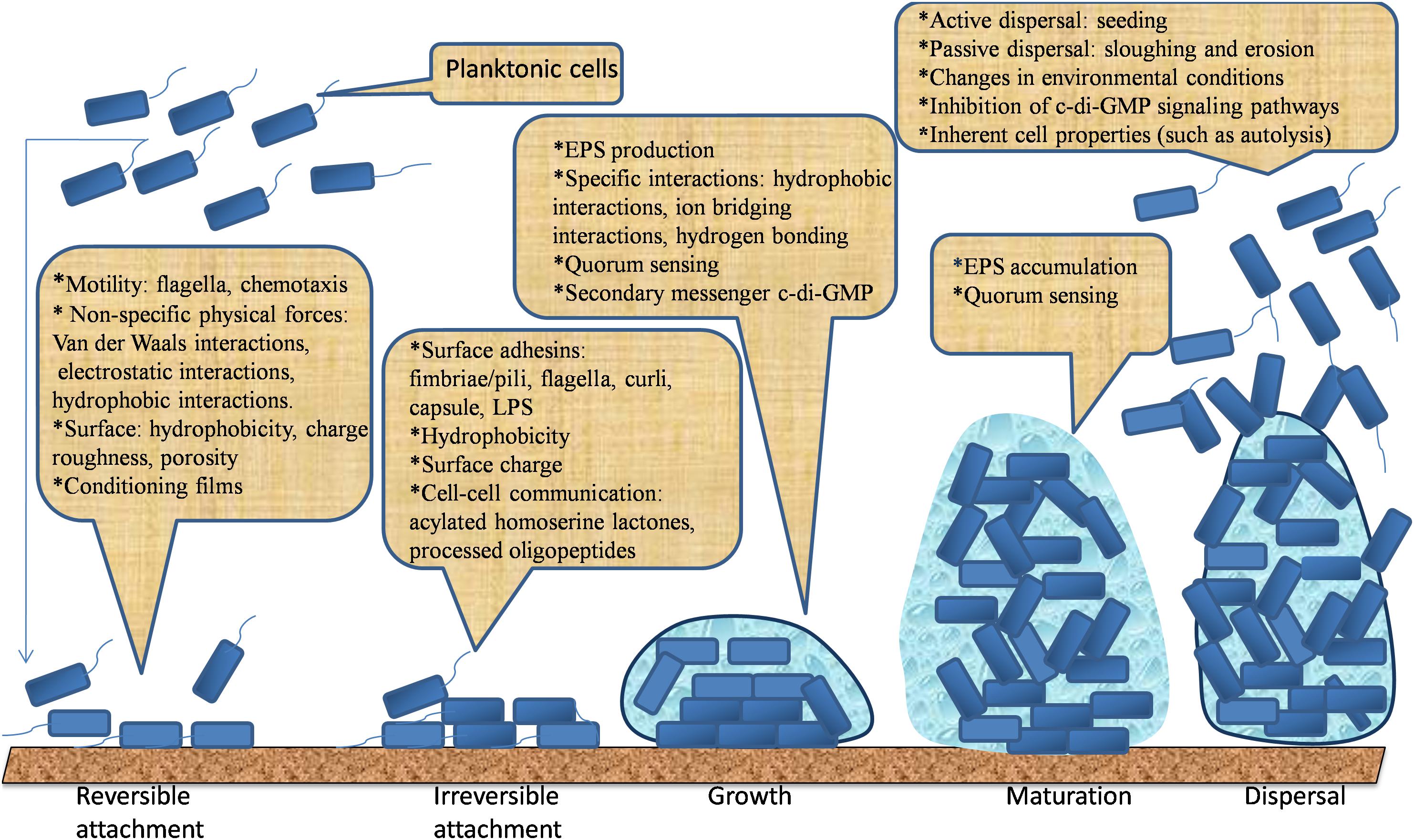
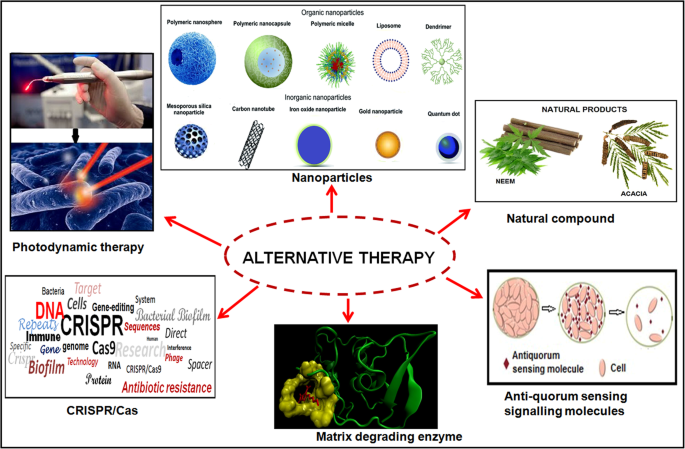
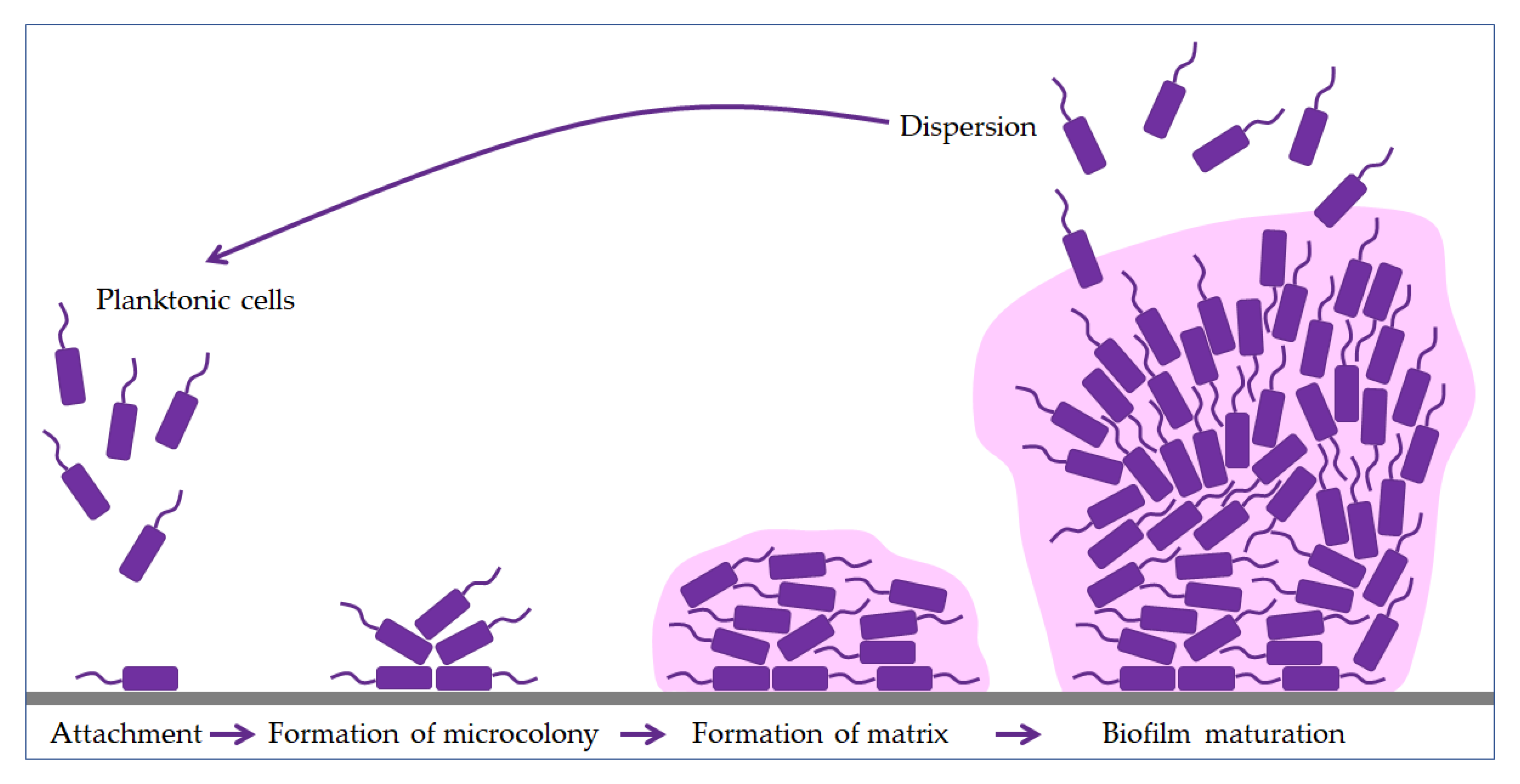
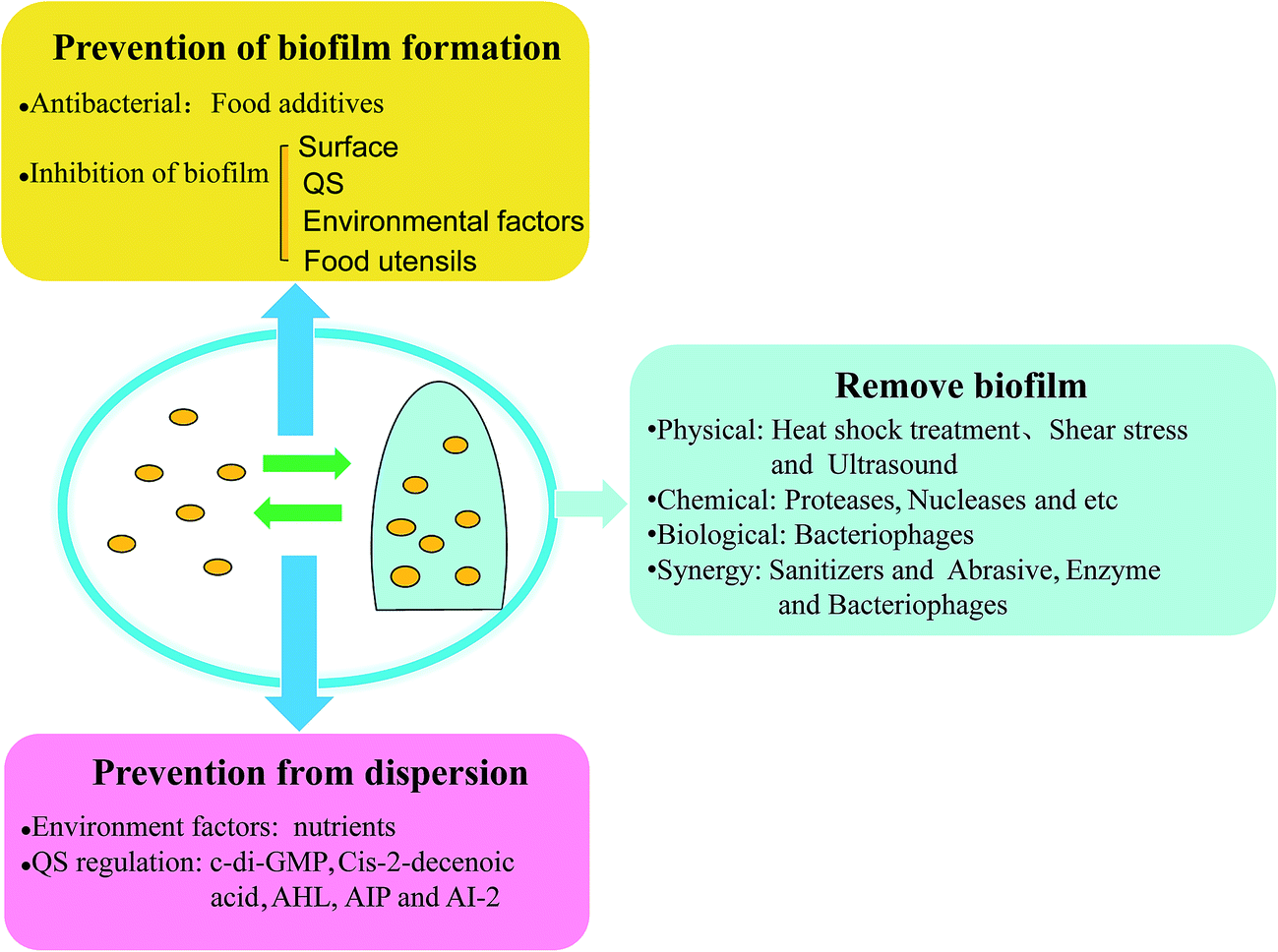
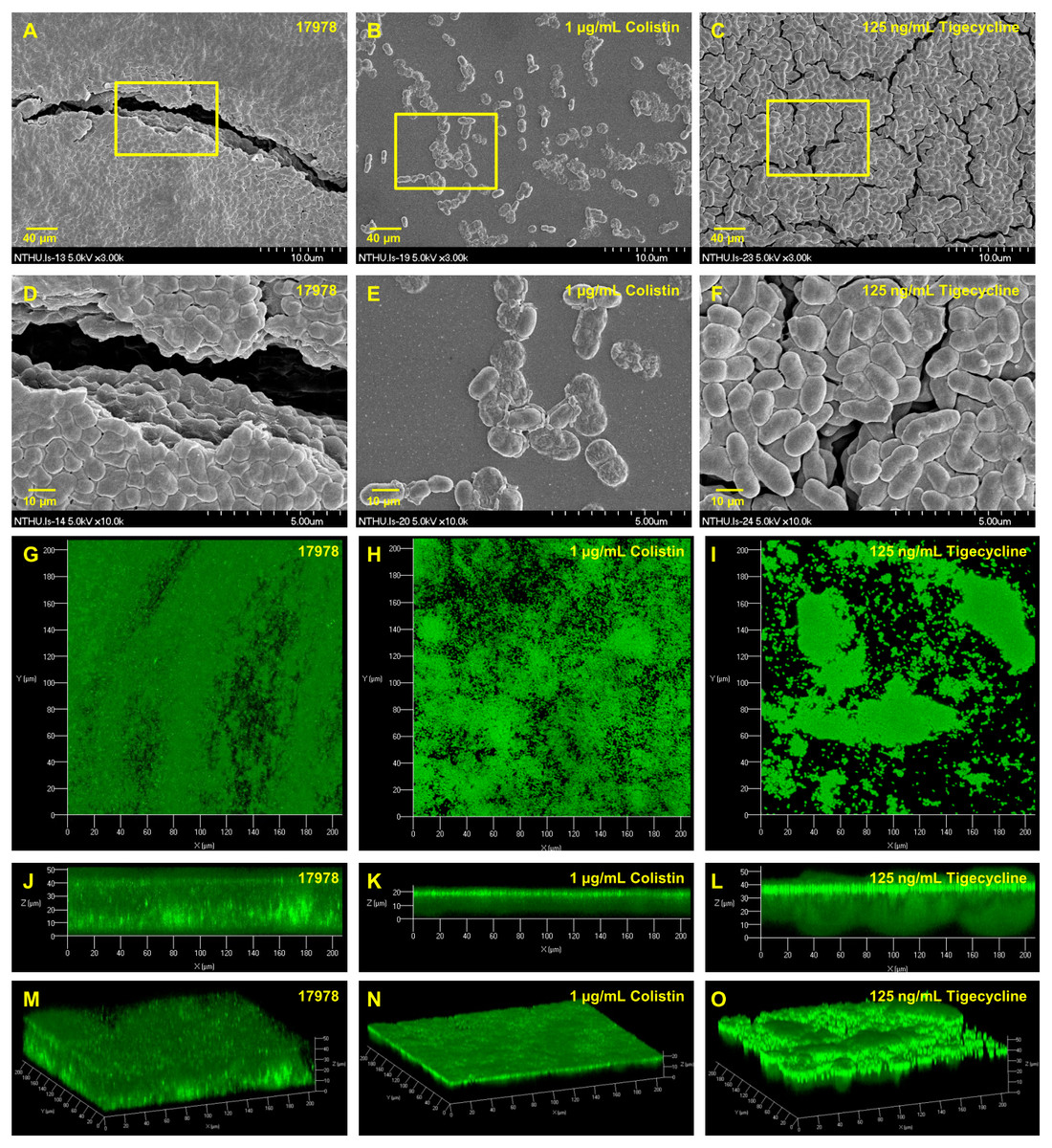
Promising strategies may include the use of compounds which can dissolve the biofilm matrix and quorum sensing inhibitors which increases biofilm susceptibility to antibiotics and phagocytosis. The process of biofilm formation consists of many steps starting with attachment to a living or non-living surface that will lead to formation of micro-colony giving rise to three-dimensional structures and ending up after maturation. Biofilms can be prevented by antibiotic prophylaxis or early aggressive antibiotic therapy and they can be treated by chronic suppressive antibiotic therapy.
How are these related to new discoveries in intracellular bacterial communication and cooperative behaviors. Bacterial biofilms are resistant to antibiotics disinfectant chemicals and to phagocytosis and other components of the innate and adaptive inflammatory defense system of the body.
Kindly login to access the content at no cost.
Characteristics of biofilms that can be important in infectious disease processes include a detachment of cells or biofilm aggregates may result in bloodstream or urinary tract infections or in the production of emboli b cells may exchange resistance plasmids within biofilms c cells in biofilms have dramatically reduced susceptibility to antimicrobial agents d biofilm-associated. Formation of biofilm is a survival strategy for bacteria and fungi to adapt to their living environment especially in the hostile environment. It is important to note that A biofilm is a structured consortium of bacteria embedded in a self-produced polymer matrix consisting of polysaccharide protein and extracellular DNA. Biofilms are implicated in more than 80 percent of chronic inflammatory and infectious diseases caused by bacteria including ear infections gastrointestinal ulcers urinary tract infections and. It is known for example that persistence of staphylococcal infections related to foreign bodies. How are these related to new discoveries in intracellular bacterial communication and cooperative behaviors. Kindly login to access the content at no cost. The impact of a foreign implant on the infection process was already recognized in 1956 as the presence of a foreign material required a 7510 4 lower dose of Staphylococcus aureus to cause a subcutaneous infection in humans which even then did not resolve 3. Transitioning from acute to chronic infection is frequently associated with biofilm formationBacteria in biofilms are innately more resistant to antimicrobial agents.
Nitric oxide has also been shown to trigger the dispersal of biofilms of several bacteria species at sub-toxic concentrations. Transitioning from acute to chronic infection is frequently associated with biofilm formationBacteria in biofilms are innately more resistant to antimicrobial agents. Characteristics of biofilms that can be important in infectious disease processes include a detachment of cells or biofilm aggregates may result in bloodstream or urinary tract infections or in the production of emboli b cells may exchange resistance plasmids within biofilms c cells in biofilms have dramatically reduced susceptibility to antimicrobial agents d biofilm-associated. Under the protection of biofilm microbial cells in biofilm become tolerant and resistant to antibiotics and the immune responses which increases the difficulties for the clinical treatment of biofilm. Characteristics of biofilms that can be important in infectious disease processes include a detachment of cells or biofilm aggregates may result in bloodstream or urinary tract infections or in the production of emboli b cells may exchange resistance plasmids within biofilms c cells in biofilms have dramatically reduced susceptibility to antimicrobial agents d biofilm-associated. Biofilms are implicated in more than 80 percent of chronic inflammatory and infectious diseases caused by bacteria including ear infections gastrointestinal ulcers urinary tract infections and. Promising strategies may include the use of compounds which can dissolve the biofilm matrix and quorum sensing inhibitors which increases biofilm susceptibility to antibiotics and phagocytosis.






















Posting Komentar untuk "How Can Biofilm Formation Impact Treatment Of Infectious Disease"